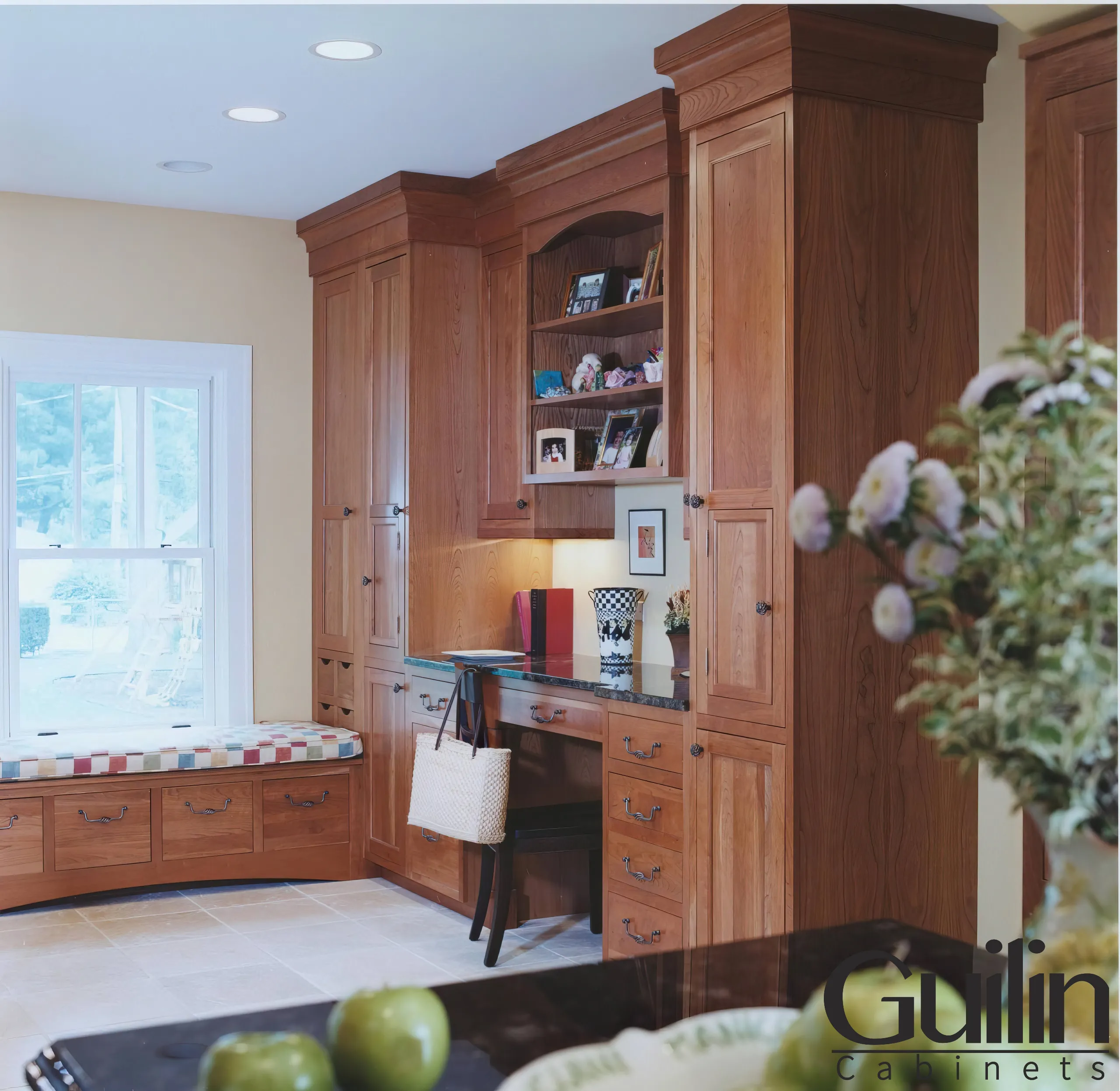
Are you currently in the process of redecorating your kitchen or looking for ways to freshen up your current space? With so many cabinet materials options on the market, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one for your home. But fear not, we’ve done the research for you. In this blog post, we’ll be diving into the world of thermofoil cabinets, laminate, and melamine – the three most popular and affordable options for cabinets. Understanding the differences between these materials and their unique advantages can make all the difference in choosing the perfect fit for your home. So let’s take a closer look at why these materials matter and what you should consider when making your final decision.
=> Read more: 10 Common Cabinet Materials: How To Choose Right!
What is Thermofoil:
Thermofoil is the name of the outside layer. The cabinets are created using a type of flexible vinyl material that is heated and vacuum-sealed to a substrate material. This produces a smooth, seamless finish that resembles painted wood, that is resistant to chipping and peeling. Thermofoil isn’t applied directly to the wood. Instead, it’s applied to a medium-density fiberboard (MDF) surface, which is a man-made product created with wood fibers, wax, and resin. Thermofoil cabinets are popular because they are cost-effective and easy to clean. However, they can be sensitive to heat and can become damaged if not properly cared for.
=> Read more: Thermofoil Wood Cabinets: Pros and Cons
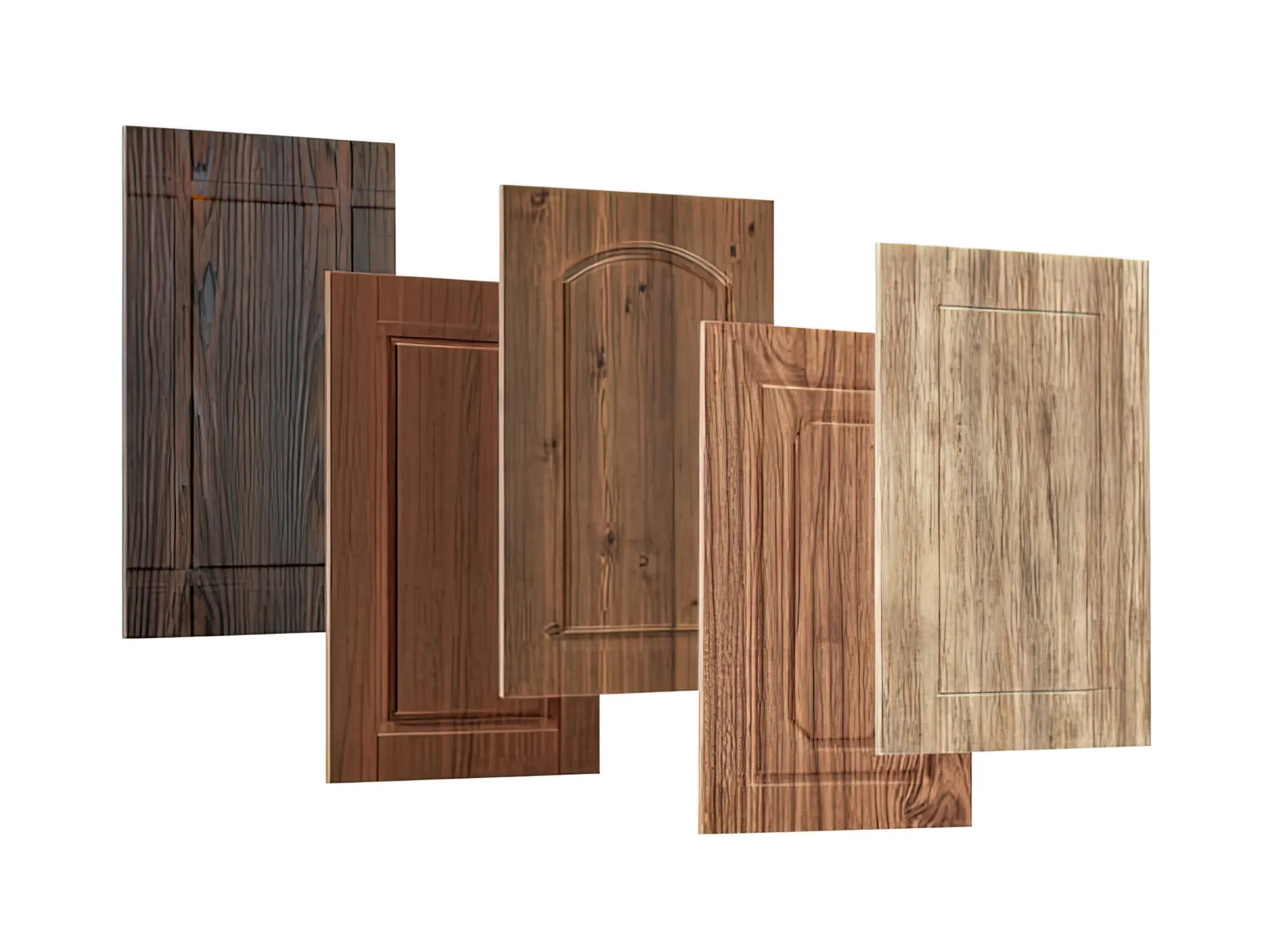

What is Laminate:
Laminate (also called Formica) is the name of the outside layer. They are made from a blend of particleboard, resin, and paper materials that are bonded together and then covered with a laminate coating. This creates a durable and stylish finish that can withstand wear and tear, making it a great option for busy households. Laminate is a surface material made from paper and resin, pressed together under heat. The quality of the laminate used can greatly affect the end product. High-pressure laminate (HPL), manufactured under 1400psi, will provide a strong and durable finish, less likely to chip and crack over time. Low-pressure laminate is less expensive, but also less durable, so it’s important to consider your needs and budget when choosing the right laminate for your project.
=> Read more: Laminate Wood Cabinets: Pros and Cons

What is Melamine:
Melamine is the name of the outside layer. it’s thermally fused onto particleboard, MDF, or fiberboard core and forms a hard outside layer to help increase resistance to moisture, heat, stains, chipping, peeling, and delamination of engined wood. It is technically a type of laminate product but is different enough to be considered a separate option. The production cost of melamine is relatively lower than that of laminate, although it is made using the same process as paper and resin. Melamine surfaces come in varying grades of quality, just like laminate. The lower quality melamine surfaces usually do not last as long as most laminate options, while the thicker textured thermal-fused melamine offers a similar life expectancy as high-pressure laminate. This makes it a popular choice for cabinet doors with its three-dimensional texture options.
=> Read more: Melamine Cabinets: Pros and Cons to Consider

What Difference Between Them
Melamine vs. Laminate
Comparison of Laminate and Melamine Prices
| Surface Type | Price |
|---|---|
| Laminate | More expensive than Melamine surfaces. The price varies based on color, texture, post-forming laminate sheets, and High Gloss (HG) monochromatic sheets. |
| Melamine | Relatively affordable. The price varies depending on color, thickness, etc. |
Colors and Wood Grains of the Two Surface
| Surface Type | Colors | Wood Grains |
|---|---|---|
| Laminate | Wide variety of colors, including metallic and glossy finishes. | Simulates many beautiful natural wood grains like cherry, oak, pine, walnut, etc. Also includes fabric and stone textures. |
| Melamine | Diverse color range, from light to dark shades. | Common wood grains like oak, walnut, teak, pine, etc. Less variety in textures compared to Laminate. |
Manufacturing Process
| Surface Type | Manufacturing Process |
|---|---|
| Laminate | Decorative paper is coated with melamine glue. The overlay is impregnated to become transparent, revealing the grain of the decorative paper during pressing. The treated papers are cut to size. Multiple layers of kraft paper are compressed under high heat, then cut to size. Finally, the overlay, decorative paper, and kraft paper are pressed together under heat and pressure to form the finished Laminate sheet. |
| Melamine | Decorative paper is printed with patterns or colors, then coated with UF (Urea Formaldehyde) glue, dried, and further impregnated with MF (Melamine Formaldehyde) glue before being dried again. The paper is then cut to the required size and packed. |
Composition
| Surface Type | Composition |
|---|---|
| Laminate | Composed of three layers: Overlay, Decorative Paper, and Kraft Papers. Overlay: Made of pure cellulose, providing shine and protecting inner layers. Decorative Paper: Provides the texture and color, coated with melamine and pressed with Overlay under high heat and pressure. Kraft Papers: Multiple layers compressed under high heat to add thickness, made from paper pulp and additives. |
| Melamine | Consists of a base paper layer and a melamine glue layer. Base paper: Made from wood pulp, titanium, and other substances to enhance durability. Melamine glue: Protects the board and provides resistance to scratches, wear, and moisture. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Type
| Surface Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Laminate | Wide color range, including metallic and glossy finishes. Wide variety of wood grains, textures, and embossed patterns. High aesthetic appeal and durability. Post-forming flexibility allows for easy shaping and installation. Good resistance to heat, impact, scratches, fire, and moisture. Available in various collections to suit different architectural spaces and customer needs. | Relatively high cost. Requires modern technical skills and equipment. |
| Melamine | More affordable than Laminate. Good resistance to scratches, fire, and water. Effective in protecting the wood core from external factors like termites and chemicals. Simple and quick production and processing. High applicability. | Less diverse colors and textures compared to Laminate. Limited flexibility in shaping for complex designs. Lower wear resistance compared to other materials. |
Applications
| Surface Type | Applications |
|---|---|
| Laminate | Coating industrial wood cores: particle board, MDF, HDF. Used in laminate-pressed pictures, decorative laminate sheets, and designing furniture for homes, public spaces, offices, hotels, shopping centers, etc., such as cabinets, tables, doors, beds, etc. Suitable for architectural spaces ranging from simple to luxurious and modern. |
| Melamine | Coating industrial wood cores: particle board, MDF, HDF. Used in designing furniture for homes, public spaces, workplaces, etc. Applicable in various architectural spaces. |
Melamine Vs. Laminate Vs. Thermofoil
As we know, Melamine is a low-pressure laminate (LPL) because it is made with a pressure of 300-500 psi (pounds per square inch). Laminate (also called Formica) is a High-pressure laminate (HPL), also called Formica, and is made with over 1400 psi (pounds per square inch).
| Material | Used For | Durability | Moisture Resistance | Heat Resistance | Price & Resale Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laminate | Veneer | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Based on cabinet core material |
| Melamine | Veneer | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Based on cabinet core material |
| Thermofoil | Veneer | Low | Moderate | Low | Based on cabinet core material |
| Property | Laminate | Melamine | Thermofoil |
|---|
| Material Composition | Multi-layered: Decorative paper, overlay, kraft paper, fused under high pressure and heat. | Decorative paper on substrate (particleboard/MDF) sealed with melamine resin. | Vinyl layer vacuum-pressed onto MDF, creating a seamless, flexible coating. |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to scratches, heat, and moisture. Suitable for high-traffic areas. | Good resistance to scratches, moisture, and heat, but less durable than laminate. | Moderate durability, moisture-resistant but susceptible to heat damage (peeling/warping). |
| Aesthetic Variety | Extensive range of colors, textures, and patterns. High gloss, matte, and textured finishes available. | Limited variety of solid colors and wood grains. Finishes are generally simpler and more uniform. | Limited colors and patterns. Provides a seamless, smooth finish, often in high-gloss or wood-grain looks. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to durability and variety. | More affordable, cost-effective for budget-conscious projects. | Economically priced, falls between melamine and laminate in cost. |
| Applications | Ideal for countertops, cabinets, furniture in both residential and commercial spaces. | Commonly used in cabinetry, shelves, and furniture for budget-friendly projects. | Often used in kitchen/bathroom cabinetry and furniture for a seamless appearance. Best away from heat. |
| Advantages | Durable, wide design variety, heat and scratch-resistant, ideal for high-traffic areas. | Cost-effective, good moisture and scratch resistance, easy to clean. | Seamless finish, moisture-resistant, easy to clean, good for modern designs. |
| Disadvantages | Edges can peel if not sealed properly, more expensive. | Less durable than laminate, limited design options, can chip or crack more easily. | Susceptible to heat damage, limited design variety, potential for peeling or warping over time. |
Durability:
- Thermofoil cabinets are made of a thin layer of vinyl that is thermoformed and glued onto an MDF (medium-density fiberboard) or particleboard. This makes them resistant to moisture, stains, and scratches, making them ideal for use in high-moisture areas like kitchens and bathrooms.
- Laminate cabinets, on the other hand, consist of a thin layer of decorative paper that is fused onto a substrate using high heat and pressure. They are durable but can be prone to chipping and peeling along the edges.
- Melamine cabinets have a similar construction as laminate cabinets but are thicker and more robust covering.

Resale Value:
Melamine, laminate, and thermofoil cabinets are all considered low-end or mid-range options. As such, they do not add much resale value to your home. However, melamine and laminate cabinets are generally perceived as higher quality and more durable than thermofoil, which can negatively impact their resale value.

Aesthetics:
In terms of aesthetics, all three materials offer a wide range of colors and finishes. Thermofoil cabinets can mimic the look of wood, while laminate cabinets can mimic the look of stone, metal, and wood grains. Melamine cabinets can also come in a variety of patterns and textures, but they are mostly used in utilitarian or commercial settings.
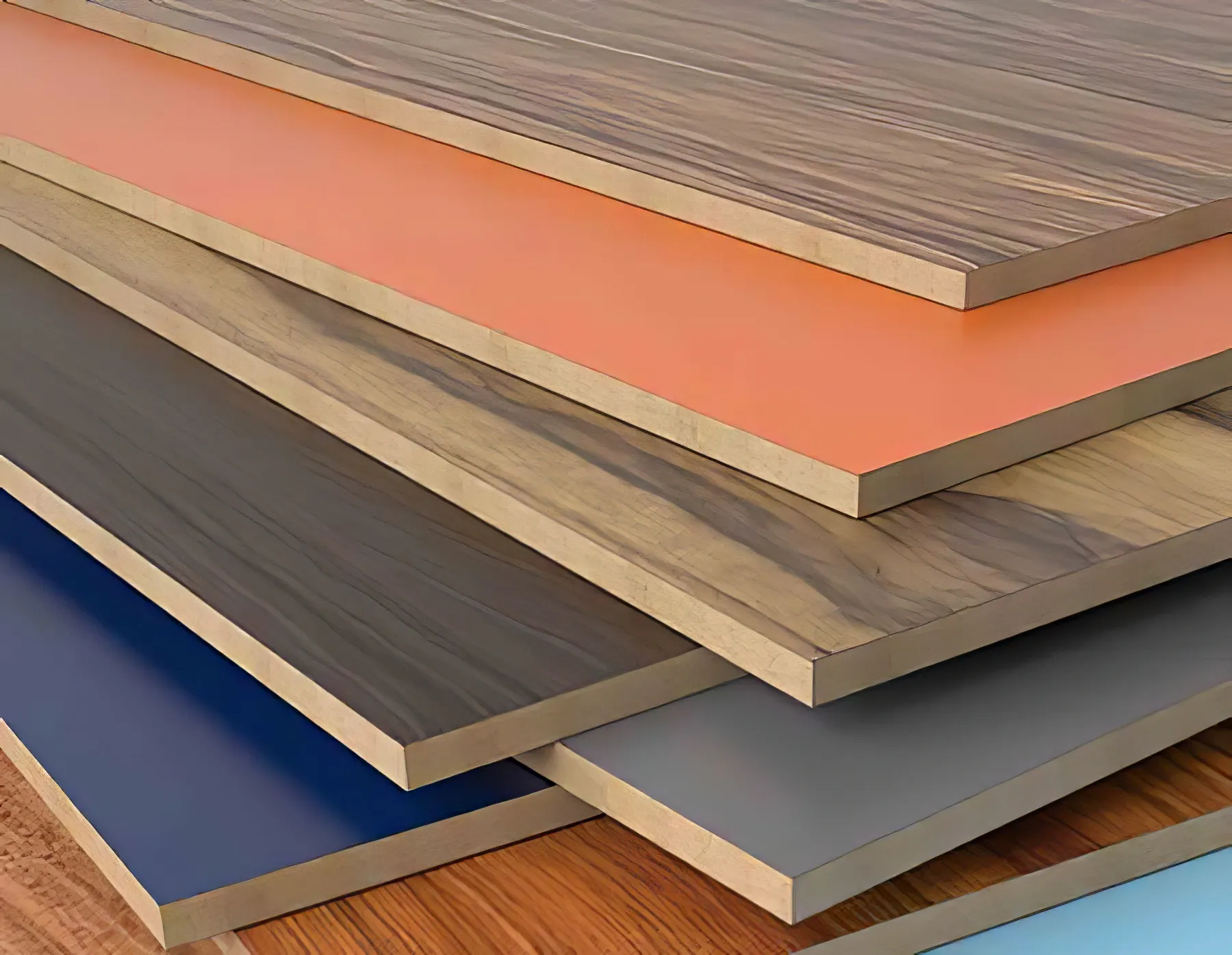

Cost:
Thermofoil cabinets are the most affordable option, followed by laminate and melamine. However, it’s worth noting that the cost of installation can vary depending on the complexity and size of your project. Additionally, the quality of the materials used can greatly affect the overall cost.

FAQs – About Thermofoil vs Laminate vs Melamine Cabinets
In Short, What is the difference between thermofoil, laminate, and melamine cabinets?
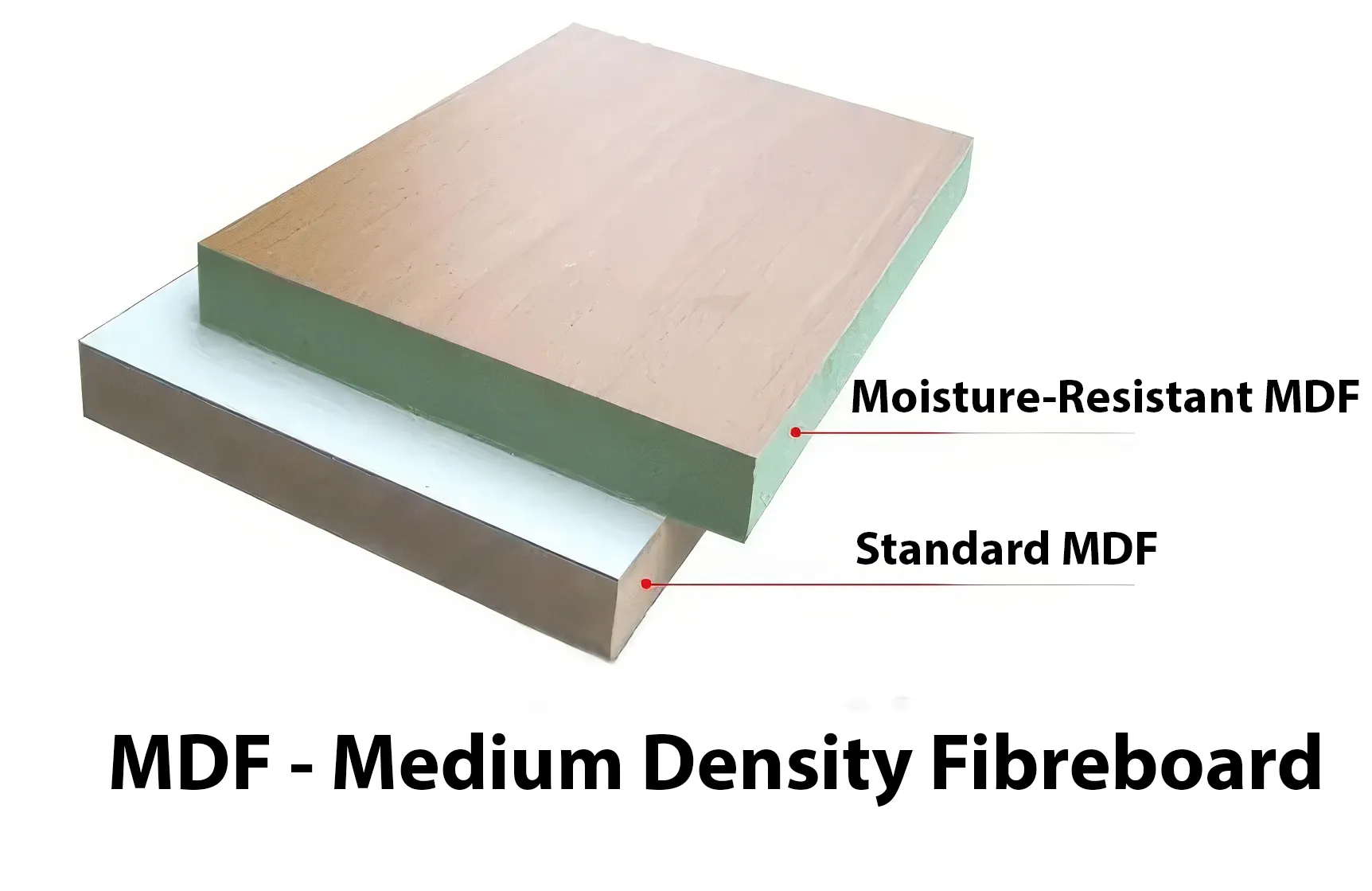

Thermofoil cabinets are made from MDF board covered with a vinyl film, while laminate cabinets are made from particleboard or MDF covered with melamine resin impregnated with paper. Melamine cabinets are also made from particleboard or MDF but are surfaced with a resin coating.
Can thermofoil, laminate, and melamine cabinets be painted over?

Painting over thermofoil cabinets is difficult because the vinyl film does not accept paint easily. Laminate cabinets can be painted using certain paint types and a specific bonding primer. Melamine cabinets can also be painted but require the use of specialized paint for laminate and melamine surfaces. => Read more:
Which option offers a broader range of design options for cabinets?

Laminates offer a broader range of designs because they are available in a wide range of colors and textures that mimic natural materials such as wood and stone. Melamine cabinets are also available in a range of colors and textures, while thermofoil cabinets are typically only available in solid colors.
Which option is the best option for kitchen cabinets?
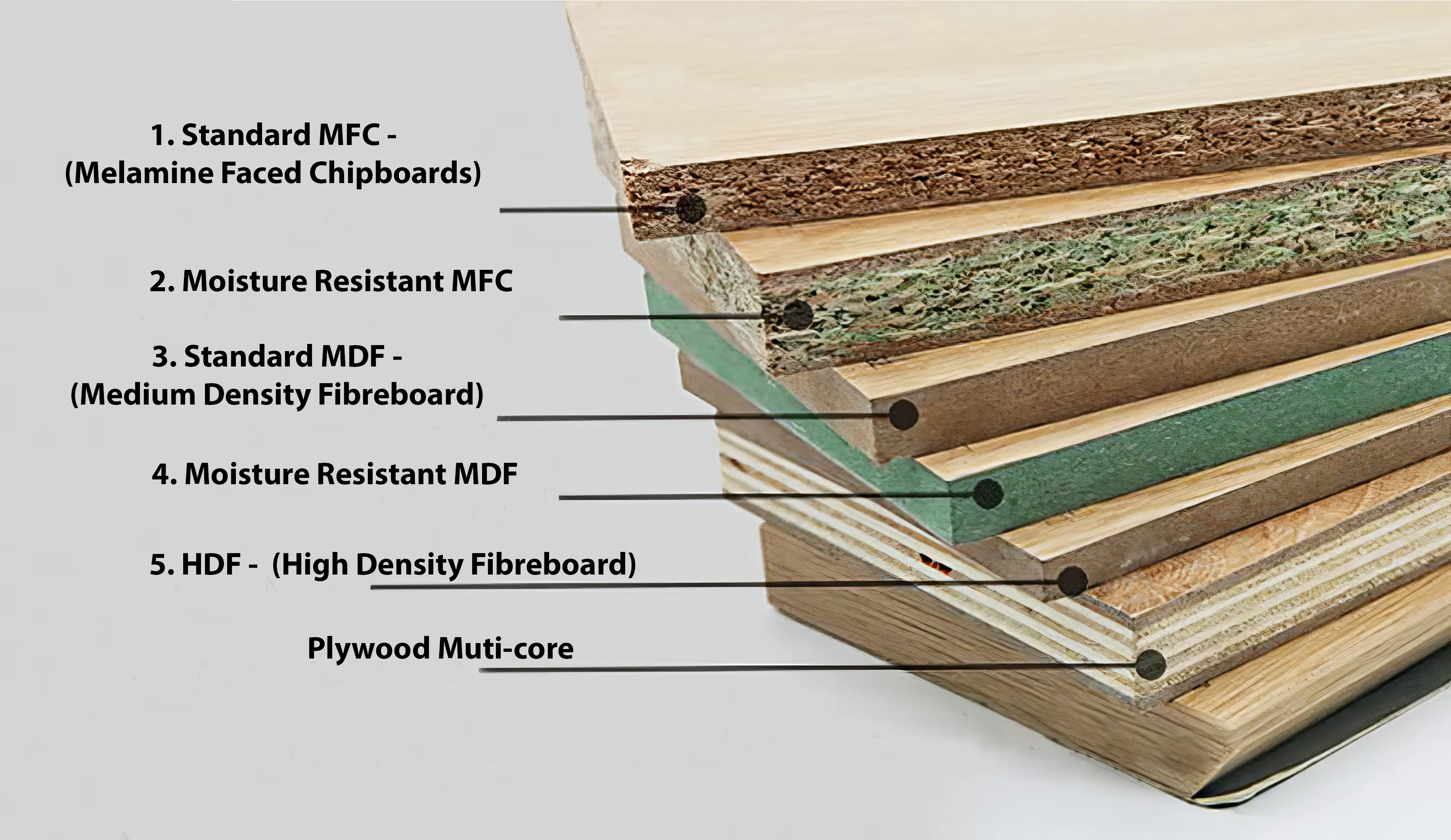
it ultimately comes down to personal preference and budget. Laminate cabinets are the most popular option for the kitchen because they are durable, and versatile and come in a wide range of colors and designs. However, if you are looking for affordability, melamine cabinets are the way to go.
How Do You Tell If Your Cabinets Are Laminate?

Vinyl laminate known as thermofoil is heated and compressed onto an MDF core. This procedure produces a surface that is flawless and devoid of any seams. Your cabinet doors may be made of laminate if there aren’t any seams visible around the joints.
















