You may have heard of HDF (High-Density Fibreboard) and MDF (Medium Density Fibreboard) as cabinet material options, but do you know the key differences between the two? In the world of cabinetry, understanding these distinctions is crucial to ensuring you select the best material for your needs. While both HDF and MDF share similarities in their composite wood fiber construction, their unique properties and intended uses set them apart significantly.
=> Read More: 10 Common Cabinet Materials
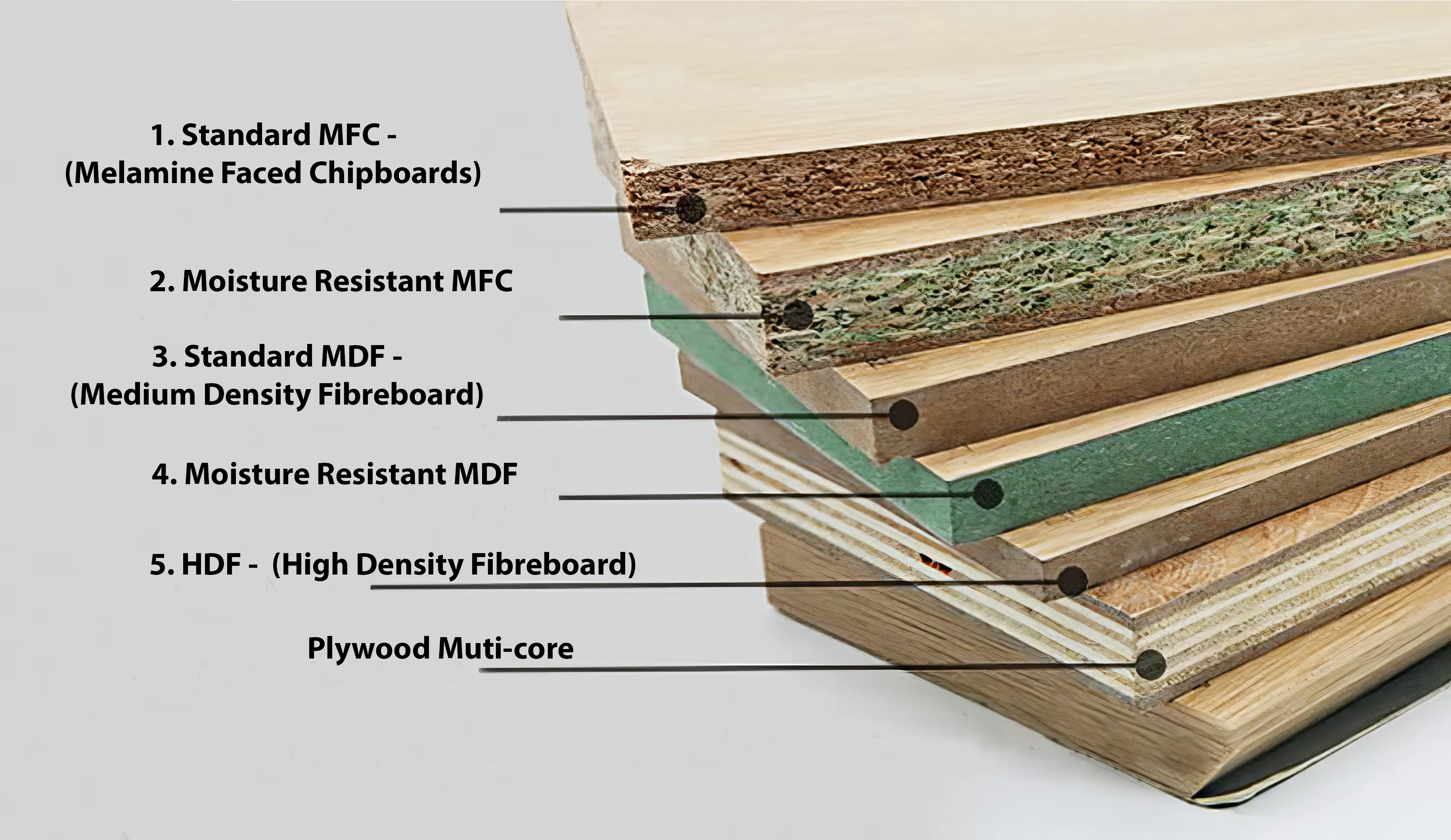
The Basics of MDF (Medium Density Fibreboard)
About MDF:
On a base level, MDF is a man-made composite panel product crafted from compressed wood fibres. It differs from HDF (High-Density Fibreboard) and is known for its typical density of 680kg/m3 – 730kg/m3 for standard-grade MDF, and 800kg/m3 for moisture-resistant MDF. MDF is a versatile material often used in the manufacturing of cabinets due to its strength and durability.
=> Read more: Medium-Density Fiberboard – MDF: Pros, Cons For Cabinets

Strengths of MDF as a Cabinet Material
To understand the strength of MDF as a cabinet material, one must consider its density. The compact nature of the fibers in MDF ensures a smooth finish when machined, reducing the likelihood of splintering or rough edges. Additionally, its density contributes to the overall durability of cabinets, making them more resistant to wear and tear over time.
=> Read More: MDF Kitchen Cabinets: Pros, Cons and Expert Recommendations

Common Uses of MDF in Cabinetry
Medium-density fiberboard (MDF) is commonly used in cabinetry for cabinet boxes, doors, drawer fronts, panel inserts, shelving, molding, end panels, toe kicks, and custom components. It’s versatile, affordable, easy to work with, and ideal for painted finishes.
=> Related Article: Why Choose MDF for Cabinets and Cabinet Doors?

The Basics of HDF (High Density Fibreboard)
About HDF:
Before exploring the distinctions between MDF and HDF in cabinet materials, understanding the basic components of HDF is the first essential step. High-Density fiberboard, or HDF for short, is a kind of composite panel product formed by humans using compressed wood fibers. With an average density of up to 900 kg/m3, it is a solid and robust substance that is harder than MDF.
=> Read More: HDF Kitchen Cabinets: Pros, Cons and Expert Recommendations

Advantages of Using HDF
In cabinetry, HDF has many benefits. Because HDF has a larger density than MDF, it is a more sturdy and long-lasting substance. Because of its compact fibers, the material is less likely to get “furry” during machining, guaranteeing a smoother finish. Furthermore, HDF’s strength and density make it perfect for withstanding bumps and knocks over time, extending the cabinets’ lifespan.

Beyond its longevity, HDF has many benefits when used in cabinets. The density of HDF also makes it possible to customize and add fine details, giving designers more possibilities. This adaptable material is a popular option for high-quality cabinets since it can be used in a variety of forms and finishes.

Common Uses of HDF in Cabinetry
Because of its exceptional strength and density, high-density fiberboard is frequently utilized in cabinetry. It is can be used in the building of shelves, drawer fronts, and cabinet doors. These parts are strong and resilient, able to tolerate wear and tear from regular use, thanks to HDF’s high density. Additionally, HDF is mostly used in laminate flooring due to its high density.

Comparing HDF and MDF
HDF and MDF serve separate yet complementary functions. The versatility of MDF makes it a popular choice for furniture and interior mouldings, whereas HDF is better suited to certain high-density applications. A misconception persists that HDF is better than MDF due to the name’s suggestion of a higher density. Nevertheless, they serve separate functions and are hence separate goods.
Different Purposes:
HDF is renowned for being strong and durability. It can be utilized to construct cabinet doors, shelves, and drawer fronts, but because of its durability and resistance to moisture, laminate flooring goods are where it is most commonly found. It’s also a popular material for door skins, giving a solid foundation for veneers or laminates, and it’s also used as underlayment, giving stability and support under flooring projects.

On the other hand, MDF, prized for its smooth surface and uniform density, is frequently employed in the manufacturing of furniture items. Its homogeneous composition makes it ideal for creating intricate designs and detailed finishes. Moreover, MDF is a popular choice for skirting boards, offering a seamless appearance when installed along the base of walls, and for architraves, providing decorative elements around doors and windows.

Density and Durability Considerations
The longevity and functionality of HDF and MDF as cabinet materials are significantly influenced by their densities. HDF is much stronger and harder than MDF, which usually has a density ranging from 680 kg/m3 to 800 kg/m3. HDF can have a density of up to 900 kg/m3. HDF’s denser composition ensures a smoother finish and better paint adhesion by reducing its tendency to become “furry” during machining. HDF is also more durable than other options for cabinets and furniture because of its higher density, which also increases its resistance to harm.
| HDF | MDF |
|---|---|
| Density: Up to 900kg/m3 | Density: 680kg/m3 – 730kg/m3 |
| Durability: Stronger and harder | Durability: Less dense, more prone to damage |
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Impact
Regarding surface quality and appearance, HDF and MDF have different qualities. Because of its high density, HDF is mostly utilized in laminate flooring; therefore, it might not be the best option for cabinet surfaces with complex finishes or intricate designs. MDF, on the other hand, is better suited for complex designs and painted finishes because to its wider density range, which improves cabinets’ overall visual attractiveness. When choosing cabinet materials, finish quality is quite important because it affects both the furniture’s longevity and final beauty, and MDF is more common than HDF in Custom Cabinetry.

Resistance to Moisture and Environmental Factors
Picking between HDF and MDF for cabinets requires careful consideration of both moisture resistance and environmental concerns. HDF may be more moisture resistant than regular MDF because of its higher density. Notwithstanding, moisture-resistant MDF versions that are resistant to moisture might offer comparable safeguarding against environmental elements, guaranteeing the durability of cabinets in diverse environments.
- Density: HDF has higher density, potentially offering better moisture resistance.
- MDF Variants: Moisture-resistant MDF can protect challenging environments.
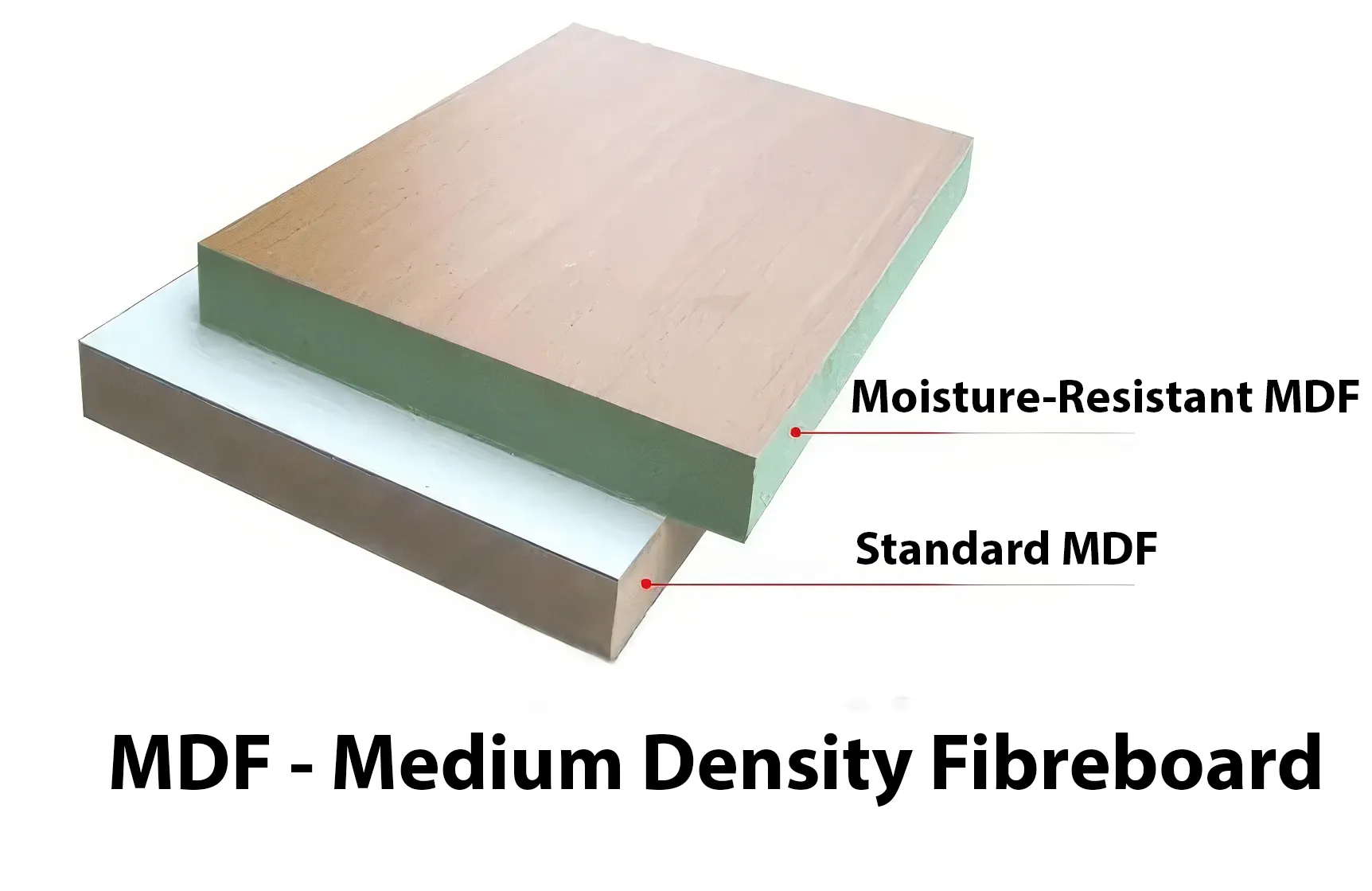

Aesthetic appeal, moisture resistance, and environmental durability are critical factors to consider when selecting the appropriate material for cabinets.
Workability and Machining Differences
The workability and machining variations of HDF and MDF should be taken into account when choosing which material to use for cabinets. HDF presents a difficulty for intricate machining and customisation because it is a denser and thinner board. But, MDF is a recommended option for complex designs and finely detailed cabinetry work due to its adaptability and simplicity of customization. Although HDF provides better durability, MDF is a more appealing option for cabinet makers who want more customisation and design flexibility due to its ease of machining and adaptability.

Price Comparison of HDF and MDF
Choosing between HDF and MDF for your cabinets should be based on your budget, as the two materials might have vastly different prices. Remember that HDF’s greater density and strength cause it to cost a little more than MDF. Nonetheless, HDF’s longevity suggests it might be a good buy.
| HDF | MDF |
| Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Greater density and durability | Less dense and durable |
| Potential long-term cost savings | May require more frequent maintenance |

Case Examples For MDF vs HDF in Cabinetry
Residential Cabinetry Projects
After considering the differences between HDF and MDF, it is evident that MDF is the more suitable choice for residential cabinetry projects. With its typical density of 680kg/m3 – 730kg/m3, moisture-resistant MDF is a durable option that can withstand knocks and bumps over time. Additionally, MDF is less likely to become ‘furry’ when machined, ensuring a smooth paint finish for your cabinetry.
Budget-Friendly Kitchen Renovation
A young couple renovating their first home opts for MDF cabinets in the kitchen. MDF’s affordability and smooth surface make it ideal for painted finishes, allowing the couple to achieve a modern look without exceeding their budget. However, they ensure proper sealing to protect against moisture near the sink and dishwasher areas.
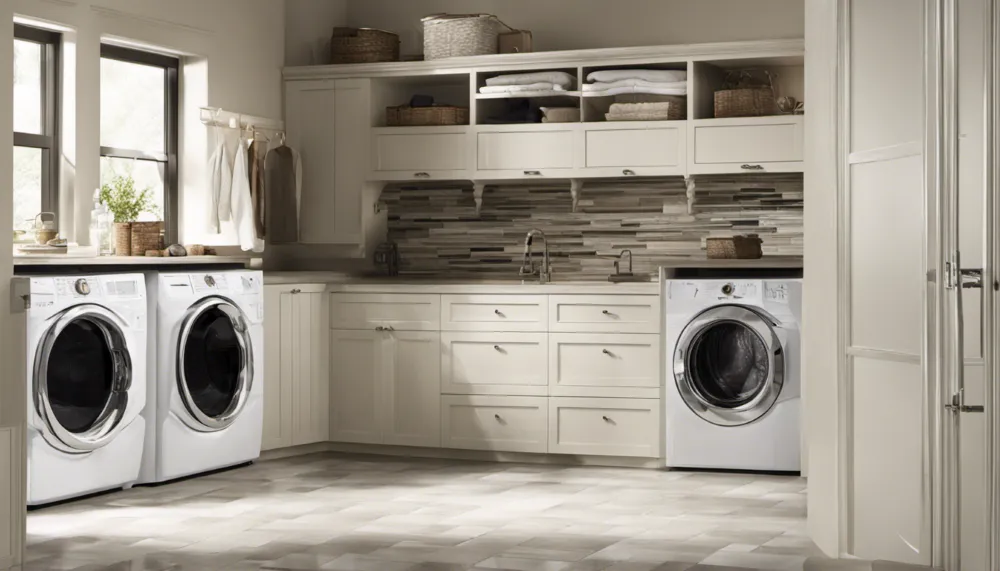

Custom Closet Systems
In a high-end residential project, the design team selects HDF for custom closet systems. HDF’s higher density provides enhanced durability, ensuring the closet components withstand daily use. Its smooth surface also allows for a flawless painted finish, aligning with the home’s luxurious aesthetic.
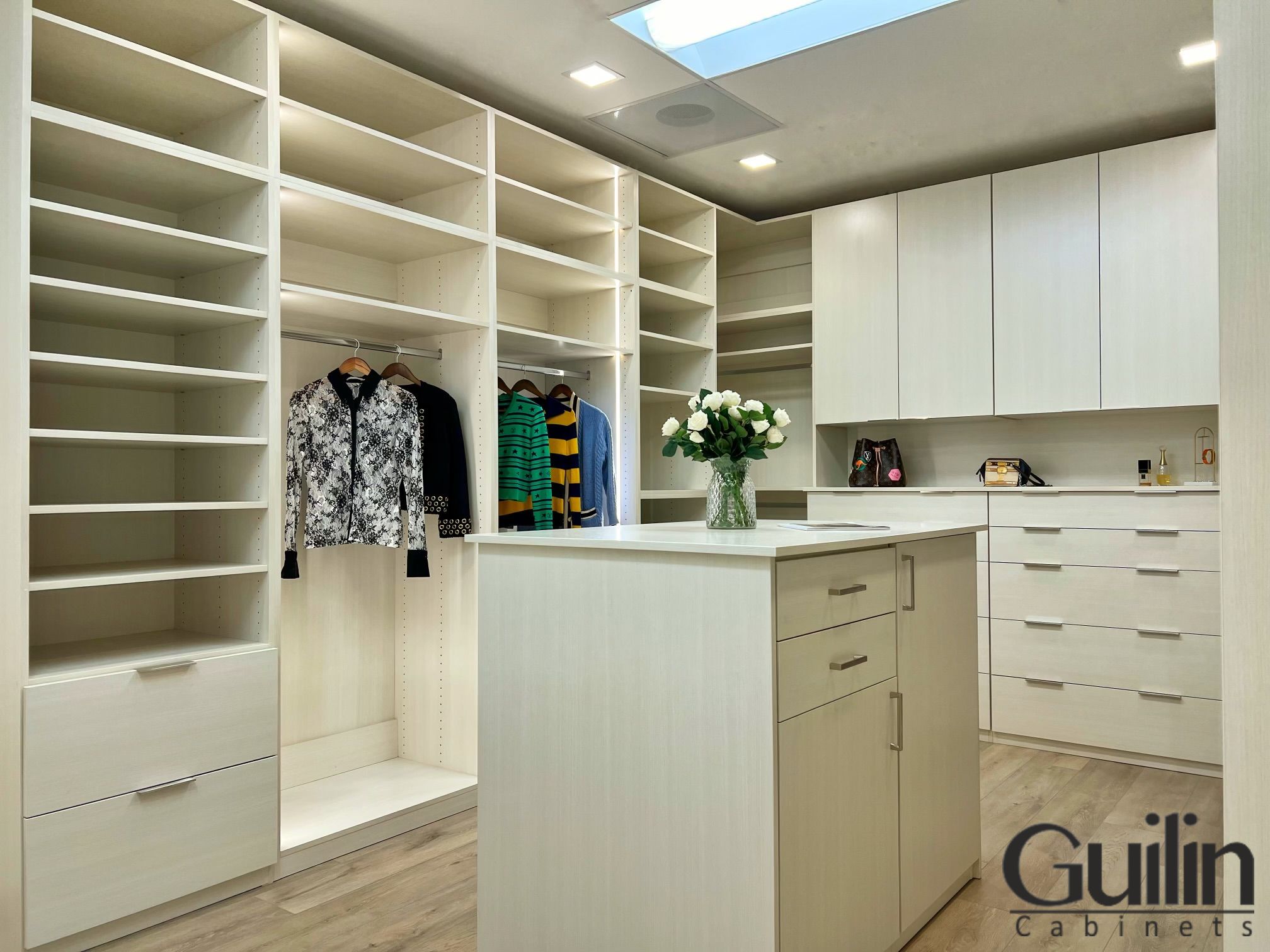

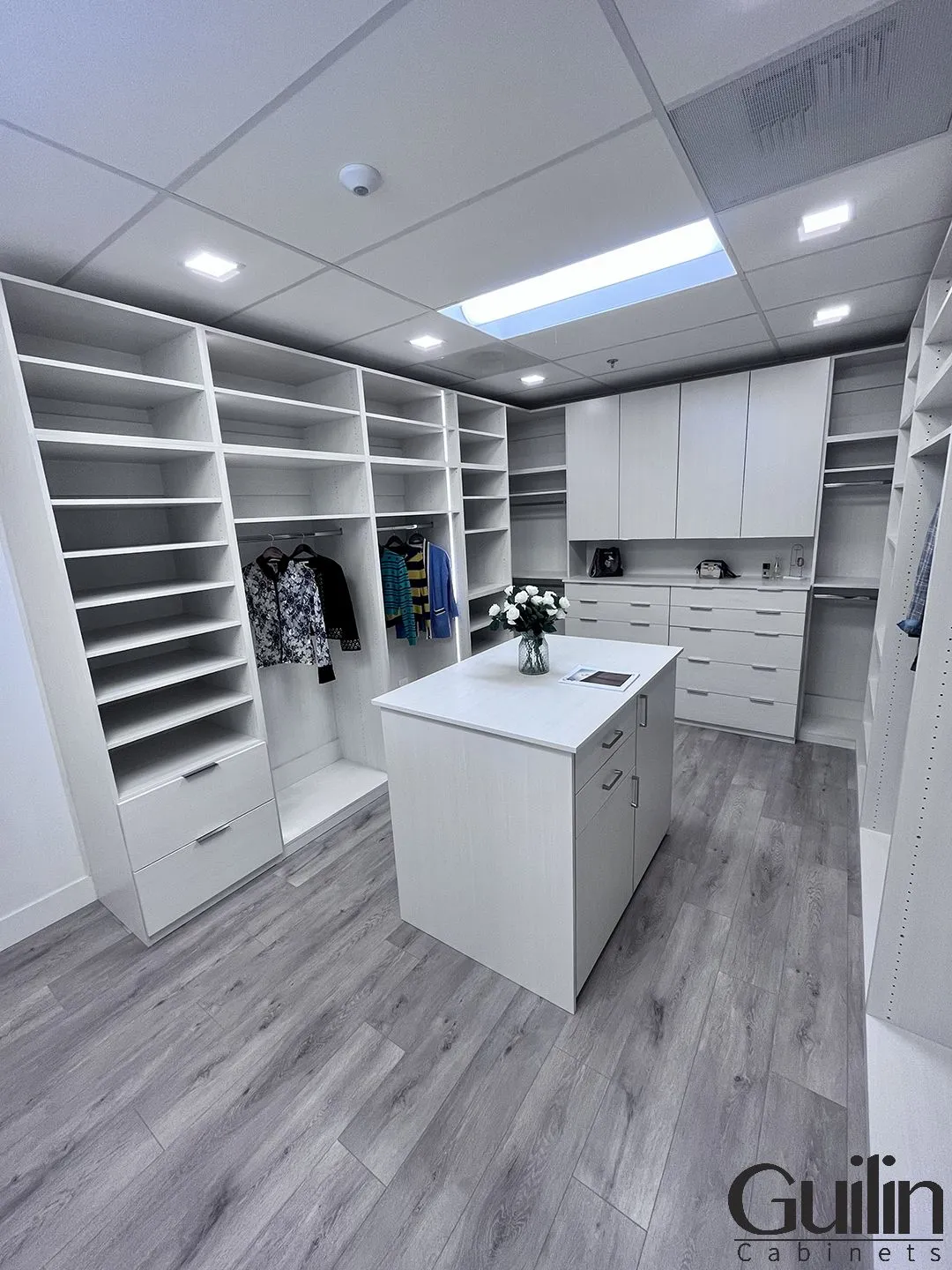
Luxury Walk-In Closet – HDF for Durability and Precision
- Location: High-end condo renovation
- Material Used: HDF for shelving, drawer fronts, and built-in organizers
- Why HDF? The client requested a sleek, painted grey finish with high durability. HDF provided a denser, smoother substrate that resists dents and allows for precise machining.
- Benefits: HDF held sharp edge profiles better than MDF and allowed the custom hardware to be mounted securely. It also offered higher resistance to daily wear in a high-use area.
- Result: A long-lasting, upscale storage system with a flawless finish that matched the rest of the condo’s modern interior.

Modern Farmhouse Kitchen – MDF for Cost-Effective Elegance
- Location: Suburban family home
- Material Used: MDF for cabinet doors and panels
- Reasoning: The homeowners wanted a clean, shaker-style kitchen with a painted white finish.
- Why MDF? MDF was chosen for its smooth surface which is perfect for painting, and its cost-effectiveness compared to hardwood. The panels were custom-routed for decorative detail without the cost of solid wood carving.
- Challenges: Moisture protection was needed near the sink area. A high-quality sealant and moisture-resistant base primer were applied.
- Result: A beautiful, bright kitchen that matched the desired aesthetic without send to much money.
Kids’ Bedroom Storage – MDF for Design Flexibility
- Location: Young family’s new build
- Material Used: MDF for built-in bookshelves, toy cubbies, and wardrobe doors
- Why MDF? It offered excellent paintability for bright colors and fun designs the children picked. Its customizability made it easy to create rounded corners and playful shapes.
- Consideration: Because MDF can swell if exposed to water, extra care was taken to seal all edges and surfaces.
- Result: The result was a colorful, imaginative room that the kids loved—and easy for parents to update as tastes change.

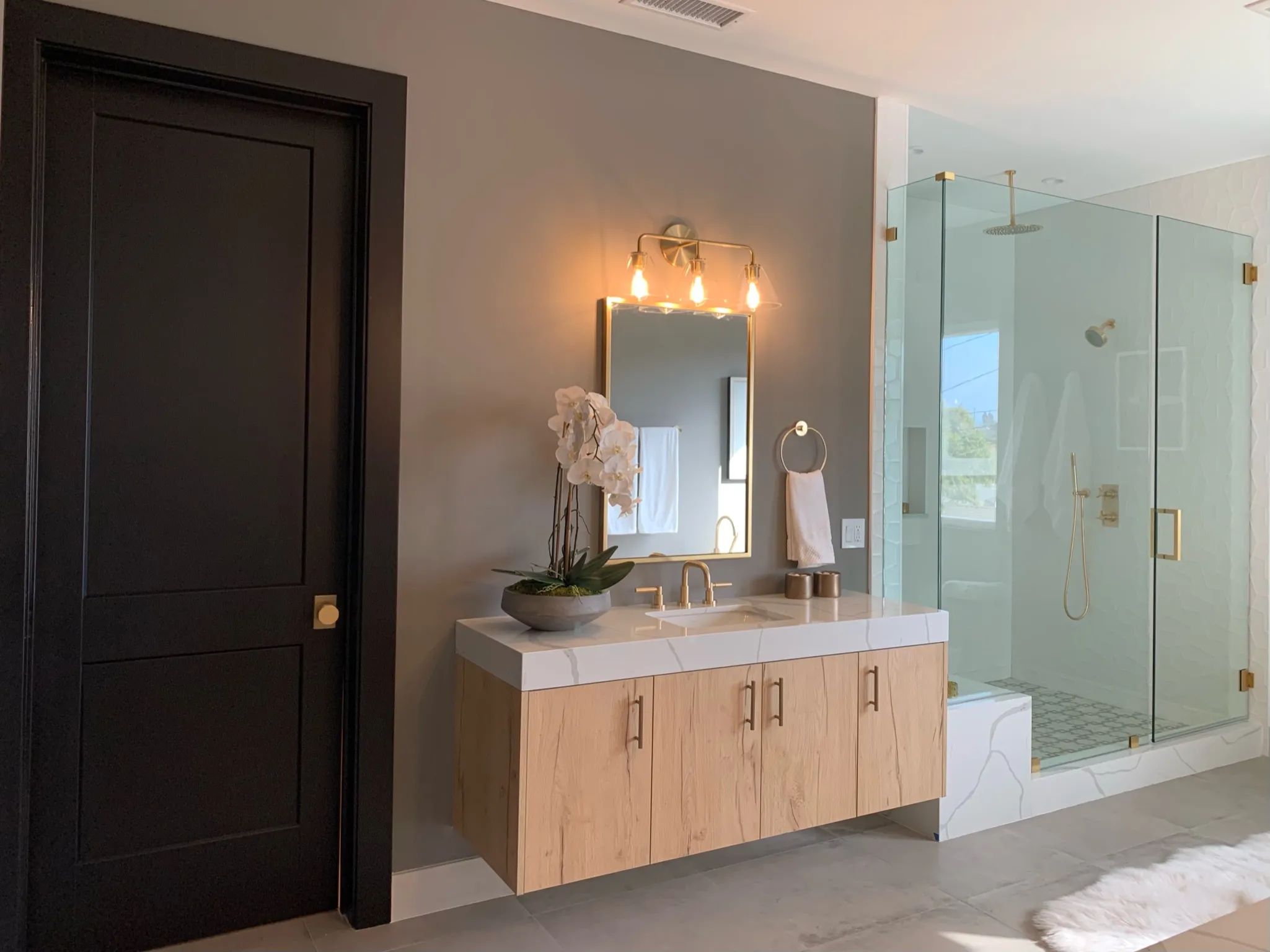
Bathroom Vanity Remodel – HDF for Moisture Resistance
- Location: Master ensuite bathroom
- Material Used: HDF for vanity doors and drawer fronts
- Why HDF? In a humid space like a bathroom, HDF was selected over MDF due to its greater moisture resistance and structural integrity.
- Features: The surface was finished with a high-gloss lacquer, highlighting HDF’s ability to hold a smooth, premium finish.
- Result: A stylish and durable vanity that performs well in a wet environment with daily use.

Commercial Cabinetry Applications
On commercial cabinetry applications, HDF may seem like a viable option due to its high density of up to 900kg/m3. However, it is crucial to note that HDF is primarily used in scenarios where extreme density is required, such as in laminate flooring, doors, cabinet doors, and door skins. For commercial cabinetry, the premium grade moisture-resistant MDF with a density of 800kg/m3 is a more practical choice, offering durability and a smooth finish for high-traffic areas.
With MDF’s proven durability and resistance to damage, it is the ideal material for both residential and commercial cabinetry projects. While HDF may have a higher density on paper, it is important to understand that each material serves a specific purpose based on its unique characteristics and strengths.
Hotel Guest Bathroom Vanities – HDF for Humidity Resistance
- Location: Coastal boutique hotel chain
- Material Used: HDF for bathroom vanity cabinets
- Why HDF? The hotel needed materials that could withstand constant moisture exposure without warping or degrading. HDF offered superior density and water resistance compared to MDF.
- Design: The vanities featured modern slab-style doors finished with semi-gloss paint to maintain a high-end look.
- Result: Durable, low-maintenance vanities that held up to daily guest use and cleaning, reducing long-term replacement costs.

Corporate Office Breakroom – MDF for Budget-Friendly Customization
- Location: Mid-size marketing agency
- Material Used: MDF for cabinetry in breakroom and utility areas
- Why MDF? The project required a budget-conscious solution that could still offer clean lines and company branding through painted finishes. MDF was easy to customize with CNC routing for logo accents and design features.
- Precautions: Moisture-prone zones near the sink and refrigerator were treated with a water-resistant sealant.
- Result: Sleek and professional cabinetry that aligned with the company’s aesthetic, delivered within a tight renovation budget.

Medical Clinic Reception Area – HDF for High-Traffic Durability
- Location: Private healthcare facility
- Material Used: HDF for built-in cabinetry and reception desk panels
- Why HDF? In an area with heavy foot traffic and frequent surface cleaning, HDF provided greater impact resistance and surface stability than MDF.
- Finish: The cabinetry was finished in a matte laminate for easy sanitation and scratch resistance.
- Result: Long-lasting reception units that kept their appearance under rigorous daily use, meeting both durability and hygiene standards.
Retail Display Fixtures – MDF for Cost and Design Versatility
- Location: Boutique clothing store
- Material Used: MDF for shelves, display cases, and cash wrap stations
- Why MDF? The store wanted custom shapes and layered designs to enhance visual merchandising. MDF’s ease of routing and affordability made it ideal for quick turnaround and frequent seasonal updates.
- Limitation: Less suitable for direct water contact, so display elements were placed away from entry points and beverage counters.
- Result: Visually striking, changeable displays that kept the store layout fresh and engaging without high costs.
Final Words: HDF VS MDF Cabinet Material
The distinction between HDF and MDF is crucial when considering cabinet materials for your project. As explained, HDF is a high-density product suited for specific uses like laminate flooring, doors,… and door skins, while MDF is a more versatile option commonly used in furniture and interior moldings.

Understanding the differences in density and durability between HDF and MDF is crucial in ensuring the longevity and quality of your cabinetry. Remember to always verify the material being used for your skirting boards and architrave, as misleading labeling can lead to subpar results. By educating yourself on these materials, you can make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable option for your needs.
FAQs About HDF VS MDF
In short, What are HDF and MDF?
HDF stands for High Density Fibreboard/Hardboard, while MDF stands for Medium Density Fibreboard. Both are man-made composite panel products manufactured from compressed wood fibers.
How do HDF and MDF differ in terms of density?
HDF is typically denser than MDF, with HDF having a density of up to 900kg/m3, while MDF has a density ranging from 680kg/m3 to 730kg/m3.
What are the common uses of HDF and MDF?
HDF is predominantly used in laminate flooring products, door skins, and underlayment, while MDF is often used in furniture, skirting boards, and architrave.
Why is density important in manufacturing skirting boards and architrave?
The density of the material impacts its durability and resistance to damage. Higher density boards are less likely to become ‘furry’ when machined and are more durable against wear and tear.
Can HDF and MDF be used interchangeably in all applications?
Maybe, HDF and MDF are different products with distinct purposes. While HDF is suitable for specific high-density applications, MDF is versatile and commonly used in furniture and interior mouldings. The name High-Density Fibreboard implies a higher density compared to Medium Density Fibreboard, leading some to believe HDF is superior. However, they are distinct products designed for different purposes.
How can one differentiate between HDF and MDF products?
Check the density of the material and refer to the data sheet or specification provided. HDF is thinner and denser than MDF, and advertising a thickness of 15mm or more as HDF is likely incorrect.
























